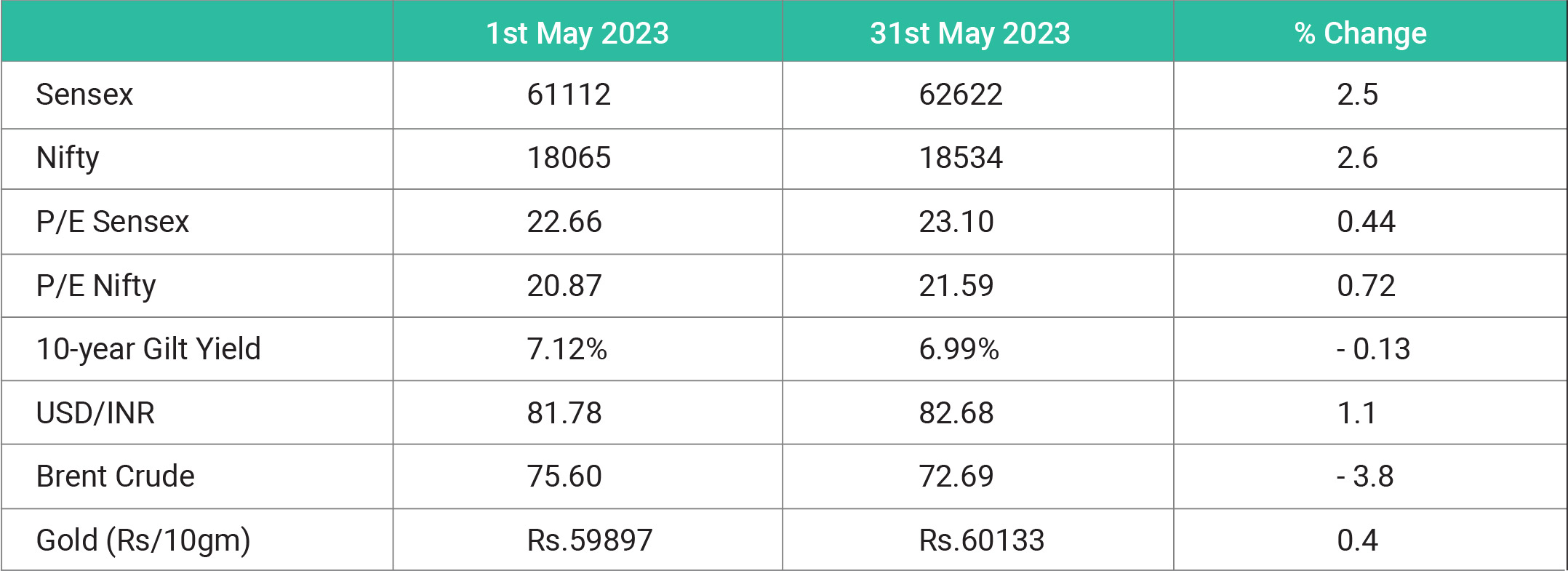
To solve the US debt crisis, the US government passed the Fiscal Responsibility Act. In other words, the bill to raise the debt limit and cap government spending in the US was passed before the default deadline of June 5. Biden signs debt ceiling bill after months-long standoff to avoid the debt default. The debt ceiling is the maximum amount of money that the United States can borrow cumulatively by issuing bonds. The ceiling was created under the Second Liberty Bond Act of 1917 and is also known as the debt limit or statutory debt limit. Suppose the US government's national debt levels bump up against the debt ceiling, in that case, the Treasury Department must resort to other extraordinary measures to pay government obligations and expenditures until the ceiling is raised again. If the debt ceiling is not raised or suspended for two years, the US government will have to cover its expenses with only its revenues. This will be big trouble as the US government will have a deficit of about US$ 900 billion this year, according to reports. The bill to raise the debt limit would allow the federal government to borrow money until after the next presidential election in November 2024. The debt ceiling has been raised or suspended numerous times over the years to avoid the worst-case scenario: a default by the US government on its debt. The recent passage of the US debt ceiling bill by lawmakers is not expected to have a significant impact on the Indian equity market, the market has anticipated that rationality would prevail, as it did in 201. Now the markets would closely await the actions of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) in its upcoming monetary policy announcement on June 8, as well as the Federal Reserve's decision on June 14. Any potential interest rate hikes would unsettle market sentiments, given the fragile state of global economic recovery and the added pressure from China on global growth," also the uncertainties over India's southwest monsoon. Many analysts believe that the Indian markets have already anticipated the US Debt ceiling issue. The bullish outlook continues due to robust GDP data, decline in commodity prices, and increased FIIs activity. There might be some profit booking in near term and the pullbacks would be a great opportunity for buyers too.......
The debt Market over the month of March 2023 stayed volatile due to the
fed rate rise and inflation numbers. With the slight decrease in the US
inflation and banking sector turmoil, the yields played around. Moreover,
the banking crisis in Europe and China’s economic revival also added
uncertainty. The upcoming MPC meeting in the first week of April may
indicate RBI may hike rates by 25bps due to poor economic numbers. The
expected 10-year benchmark yield would stay in the range of 7.25% to
7.50% in the coming months. The debt mutual funds will attract LTCG
from 1st April 2023 onwards, this would change the perspective of mutual
fund investors toward shorter to medium-duration funds. Hope that the
inflation eases and hence the interest rates may not increase in the future.
Rupee was volatile through the month of March, with the US fed rate, the
global banking crisis and the low FPIs, rising crude prices, escalation in
the Ukraine-Russia war, and lastly the export numbers. The FPIs after the
US fed rate rise are looking at less risky currency getting better returns.
Exports are low due to recession in the other world economies.
Gold prices in India have been on the rise for the past few years and can
be attributed to uncertainties including the global economy, currency
fluctuations, and changes in demand as well as supply of gold. Metals in
the commodity market can provide a hedge against inflation and currency
devaluation. Better inflation numbers could provide support to Gold prices
but would be unstable to curb the interest rate changes.

